Recently, one of my colleagues shared a fraudulent email they received from PayPal. What was interesting, is that unlike other phishing scams, this email was able to pass email authentication measures and get delivered.
While this is far from the most common form of phishing, it’s not an isolated incident—platforms like this can, and do, get abused.
Learn more about how these good email systems end up becoming vulnerable and how you can protect against them.
PayPal fraudulent email example
Here’s an example of a fraudulent delivered message:
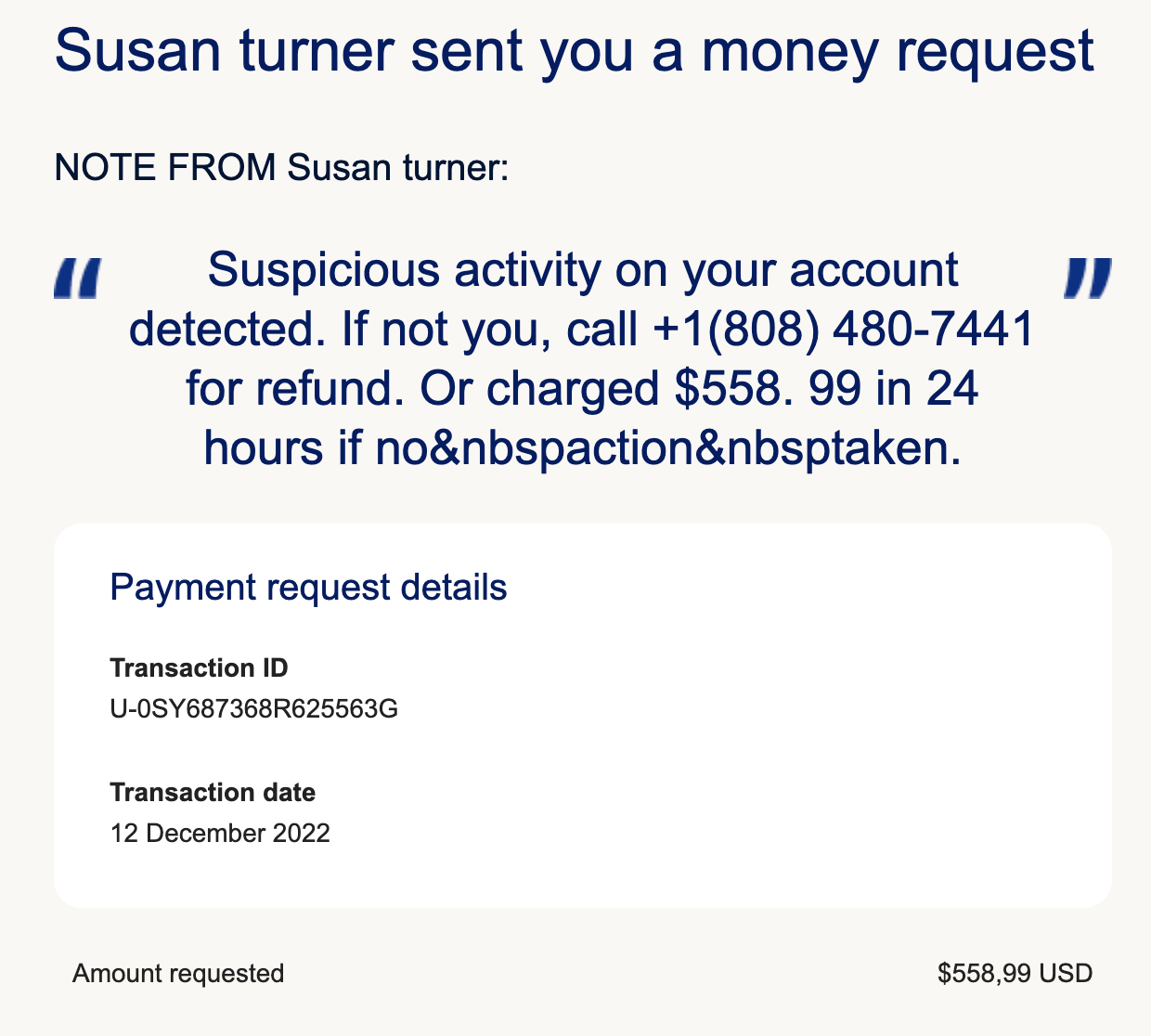
The goal of this email is ultimately to defraud the recipient and put money in the pocket of the sender, money that the sender is not entitled to.
How do bad actors send from your domain?
Because of the way PayPal and some other platforms, like LinkedIn, have configured their systems, bad actors can generate fraudulent content and then use the platform to push it to victims.
Technically, PayPal has done everything right in regards to how they send their mail. How they validate and filter content is another story. They’ve gone through the email authentication process and ensure that messages generated on their end can be delivered to the targeted recipient. We can even use Valimail’s Domain Checker to get more information about where the message came from, and we can see that the message did indeed come from a PayPal IP:
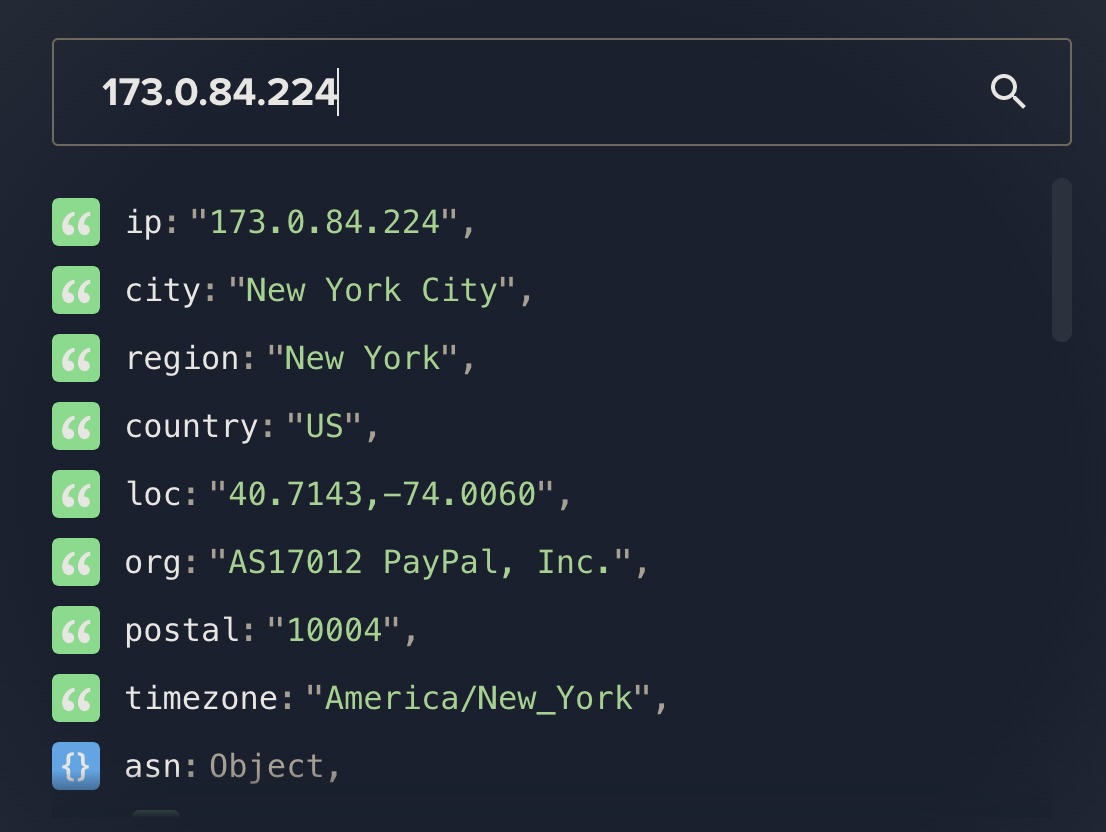
The issue is that, in this case, scammers are using PayPal to push a fraudulent message out to unsuspecting recipients. If this were an actual letter, the scammer basically got an authentic PayPal envelope, they stamped and addressed it correctly so that it arrived at its destination, but the letter inside is fraud!
How to prevent fraudulent email sending
The best way to stop these malicious attempts is to implement tighter controls on the content of the messages being sent. This, however, is easier said than done because fraudulent emails often mimic legitimate content so closely that they can be challenging to distinguish from authentic communications.
A point to remember when it comes to email authentication and DMARC, is that authenticated email means that the message is “from an authorized system,” but not necessarily “good.” For PayPal, messages like these are a common occurrence, and they even have blog posts on their end designed to help recipients.
A rule to remember here is that the bad guys only get paid when they win, so they are always, always, always going to be looking for ways to exploit the system.
To effectively prevent fraudulent email sending, organizations should consider the following measures:
- Email Authentication Protocols: Implement SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to verify that emails are sent from authorized servers and have not been tampered with. These protocols help guarantee the authenticity of the email’s origin.
- Advanced Email Filtering: Use advanced email filtering solutions that employ AI and machine learning to detect and block phishing attempts. These solutions can analyze patterns and anomalies in email content and metadata to provide an additional layer of protection.
- User Education and Awareness: Regularly educate employees and customers about the dangers of phishing and how to recognize suspicious emails. Provide clear guidelines and examples to help recipients identify fraudulent messages.
- Regular Monitoring and Reporting: Continuously monitor email traffic for unusual patterns and generate reports to identify potential threats. Regularly reviewing these reports can help in promptly addressing any security issues.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establish easy-to-use reporting mechanisms for recipients to flag suspicious emails. Quick feedback from users can help identify and mitigate threats.
- Content Controls: Implement stricter controls on the content of outbound emails. This can include scanning for common phishing elements and guaranteeing legitimate emails include specific security markers that recipients can verify.
Why you need to implement DMARC
With DMARC, domain owners can help mailbox providers identify and potentially stop fraudulent impersonation attempts that originate remotely from their platforms by publishing a strong DMARC policy record. While domain owners will still have work to do to try to stop the fraud, they’ll at least have visibility into it before it leaves their platform. The takeaways here are:
- With DMARC in place – Bad actors are forced to take more difficult and less legal approaches to abuse you, like violating your terms of services or hacking accounts, in order to send mail using your domains.
- Without DMARC in place – Fraudulent impersonation attempts can originate from anywhere, and there’s nothing the domain owner can do to prevent them. Attackers don’t need to find clever ways to abuse your domains. They can just send fraudulent email as you all day every day.
Implementing DMARC secures your domain against phishing and email spoofing attacks. Here’s how DMARC can protect your domain:
- Visibility: Gain insights into who is sending email on behalf of your domain.
- Control: Guarantee only authorized senders can use your domain.
- Security: Protect your customers and employees from phishing attacks.
Valimail provides comprehensive solutions to help you implement and manage DMARC. Our team of experts will guide you through the entire process to protect your entire domain.
- Step-by-step guidance: We provide detailed instructions and support to implement DMARC on your domain.
- Continuous monitoring: Our tools monitor your email traffic and provide real-time reports.
- Expert support: Access to our team of DMARC experts who can help you troubleshoot and optimize your email authentication.
Ready to secure your domain? Contact Valimail today to get a free demo and learn how our solutions can help you achieve DMARC enforcement.