With the constantly growing threat of cyberattacks, cybersecurity insurance has turned from a nice-to-have to a need-to-have. You wouldn’t buy a home in Florida without hurricane insurance, and you shouldn’t operate any part of your company online without cyber insurance—it’s just an aspect of doing business in the digital world.
Fortunately, you can use modern-day tools to safeguard against potential financial repercussions and fortify your digital walls. Enter Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC): a robust email authentication protocol designed to shield your domain from unauthorized use.
In 2021, Congress conducted a study of the U.S. cyber insurance market, and they found that there were policy price increases due to an increased demand along with more severe and frequent cyberattacks. Consequently, more than half of clients saw prices go up 10 to 30%.
DMARC could help lower that premium.
DMARC has proven its worth over the years, and some cybersecurity insurance providers now require it (or implement it themselves) to insure your business. Below, we’ll walk you through the ins and outs of cyber insurance and how DMARC boosts customer trust and potentially reduces your cyber insurance premiums.
What is cyber insurance?
Cyber insurance (or cybersecurity insurance) is designed to mitigate the financial impacts and assist in the recovery process following a cyber-related security breach. While it’s best to prevent acts from happening in the first place, there’s no such thing as a foolproof plan—which is why it’s important to have cyber insurance in your back pocket.
Just in case.
Components of cyber insurance
- Data Breach and Incident Response: Covers the costs related to managing a data breach, including notification, public relations efforts, and investigations.
- Business Interruption: Provides coverage for the loss of income and related costs where a cyber event causes an interruption to normal business operations.
- Extortion and Ransomware: Covers the costs of cyber extortion and ransomware attacks, including ransom payments and expenses to manage the incident.
- Legal and Regulatory Costs: Addresses the legal and regulatory repercussions following a cyber incident, including defense costs and regulatory fines.
How does cyber insurance work?
Cyber insurance operates as a safety net to provide financial and strategic support in the event of a cyber incident. But how does it work? Here’s a brief overview of the process.
1. Assessment of cyber risks
Before a policy is issued, insurers assess a business’s cybersecurity posture, evaluating its risk management practices, security protocols, and historical data related to cyber incidents.
This is where many insurers will check to see if you have DMARC at enforcement. To see the DMARC status of your domain, use our free domain checker:
Based on the risk assessment, insurers calculate the premium, which is the business’s cost for the coverage. Higher risk generally translates to higher premiums.
2. Policy issuance
Once the premium is determined, the insurer issues the policy, detailing the coverages, exclusions, limits, and deductibles, providing a clear framework of what is and isn’t covered.
The policy will specify the period during which coverage is provided, and it will need to be renewed upon expiration to maintain coverage.
3. Claim process in the event of a cyber incident
In the event of a cyber incident, the policyholder must promptly report it to the insurer, adhering to the guidelines and timelines specified in the policy. The insurer may conduct an investigation involving cybersecurity experts to assess the incident, validate the claim, and determine the extent of the coverage applicable.
Upon validation of the claim, the insurer approves it and provides financial support per the policy’s coverage, assisting in recovery, legal defenses, and other applicable areas.
Does your organization need cyber insurance?
Not sure if you need cyber insurance? That’ll depend on the nature of your business, the sensitivity of the data you handle, and your organization’s exposure to cyber risks. Here are some aspects to consider:
- Data Sensitivity and Regulatory Compliance: Handling sensitive data or adhering to strict data protection regulations like GDPR or HIPAA may necessitate cyber insurance to mitigate a breach’s potential financial and legal impacts.
- Digital Dependency: Organizations with substantial operations, transactions, or interactions occurring online may find cyber insurance necessary to safeguard against disruptions from cyber incidents.
- Financial Considerations: Evaluate your organization’s financial capability to absorb the impacts of a cyber incident, considering potential business interruptions and income loss.
- Reputation Management: Cyber insurance can be pivotal in managing the reputational fallout post-cyber incident, supporting PR efforts and customer communication to maintain trust and brand image.
- Cybersecurity Posture: Despite robust cybersecurity measures, the evolving nature of cyber threats may warrant cyber insurance as an additional layer of protection against sophisticated attacks.
- Vendor and Third-Party Interactions: Engaging extensively with vendors or utilizing third-party platforms for data management may expose your organization to additional cyber risks, making cyber insurance a necessary protective measure.
How DMARC boosts your email security
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) works by authenticating the sender’s identity, shielding your email recipients—clients, employees, customers, or partners—from malicious attempts to impersonate your domain.
Domain owners define policies within DMARC that dictate how email receivers should handle unauthenticated emails. The three policies that can be set in a DMARC record are:
- p=none: take no action
- p=quarantine: deliver to the spam folder
- p=reject: reject the message outright

These policies prevent cybercriminals from using your domain to send emails, protecting your recipients and brand from bad actors.
The relationship between DMARC and cyber insurance
DMARC and cyber insurance go hand in hand. Cyber insurance providers want to make money, and they can’t do that if they have to make payouts to all their clients with data breaches—that’s why they’re requiring clients to implement DMARC.
Here are all the ways DMARC and cyber insurance interact:
- Risk Mitigation: Implementing DMARC is a proactive step in mitigating the risk of email-based cyberattacks, which can be viewed favorably by cyber insurers because it reflects a commitment to cybersecurity best practices.
- Reducing Claim Probability: By minimizing the likelihood of phishing and spoofing attacks, DMARC indirectly reduces the probability of claims related to such incidents, making your organization a lower-risk entity for insurers.
- Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: DMARC helps organizations adhere to various data protection and cybersecurity regulations. This can be a positive factor in cyber insurance assessments, potentially influencing policy terms and premiums.
- Data Breach Prevention: DMARC helps prevent email breaches by authenticating outgoing emails and mitigating impersonation attacks, protecting your sensitive data, which is often a core concern for cyber insurers.
- Enhanced Security Posture: Organizations with DMARC implemented may be perceived as having a robust cybersecurity posture, which can be advantageous during cyber insurance negotiations and policy customizations.
- Incident Response Readiness: The reporting feature of DMARC provides insights into email-sending practices and potential threats, helping inform your organization’s incident response readiness—a factor often considered by cyber insurers.
Protect your business with Valimail Enforce
DMARC plays a pivotal role in protecting your business from cybersecurity threats and can also influence your cyber insurance coverage and premiums. However, manually implementing and maintaining your DMARC status is easier said than done. Unless you use Valimail.
Valimail Enforce provides a robust, automated, and user-friendly solution to DMARC enforcement. It guarantees that only legitimate emails are delivered from your domain, protecting your brand and customers from malicious impersonation attacks.
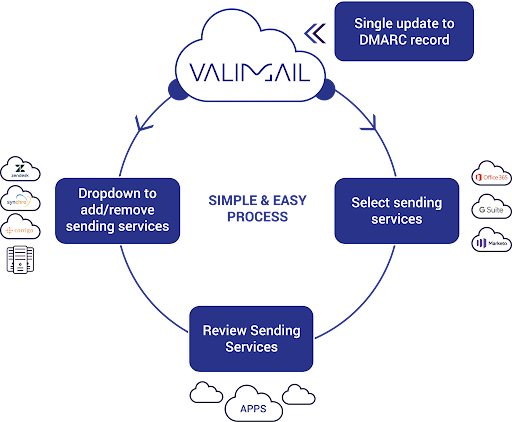
Here are a handful of other benefits, too:
- Automated DMARC: Simplify DMARC management with Valimail Enforce’s automated solutions.
- Improved Deliverability: Ensure your emails consistently reach their intended recipients.
- Strengthened Trust: Uphold your brand’s credibility with secure email communication.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigate through data protection and communication regulations effortlessly.
- Insurance Posture: Boost your cybersecurity stance in the eyes of cyber insurers.
Valimail Monitor, our free service, offers insights into your DMARC reports and identifies all senders using your domains.