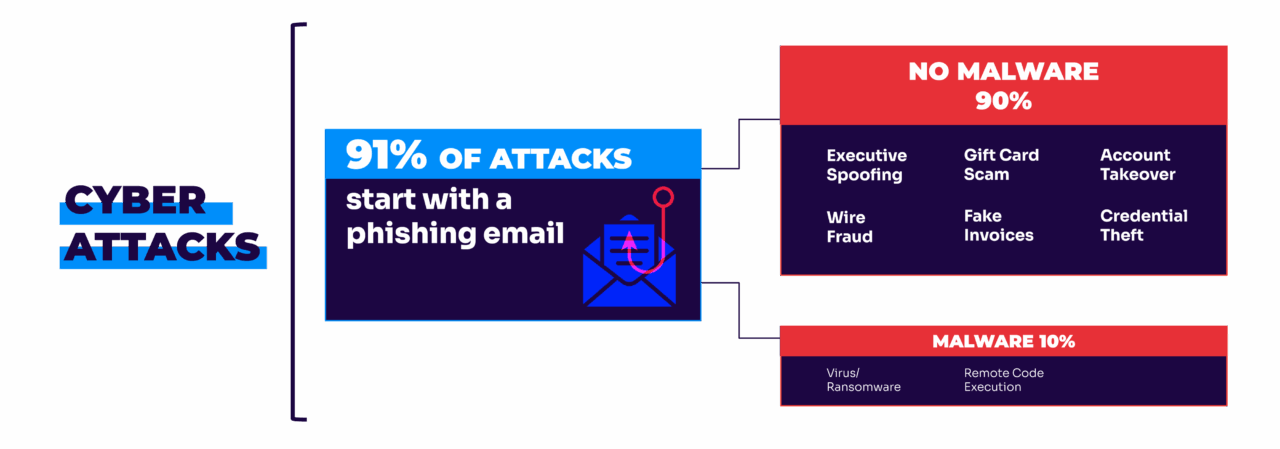
Despite all the advanced security solutions we have today, phishing emails are still the most successful way criminals breach organizations. It’s not even close. Why? Because phishing targets the one security layer technology can’t fully protect: humans.
We’ve seen companies with multi-million dollar security systems fall victim to a single convincing email. Nearly 3.4 billion phishing emails are sent every day, and the people behind them are getting smarter, more targeted, and harder to spot.
Fortunately, it’s not all doom and gloom.
There are tried-and-true tactics you can implement to spot and prevent phishing emails before they do any harm to you, your business, or your customers. Below, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about phishing emails in 2025.
What is a phishing email?
A phishing email is a fraudulent message designed to trick you into revealing sensitive information, clicking on malicious links, or downloading harmful attachments (all while masquerading as a trustworthy sender). It’s digital deception with a dangerous hook.
These aren’t yesterday’s obvious Nigerian prince scams with terrible grammar and outlandish claims. Today’s phishing emails are smart, targeted, and often nearly indistinguishable from legitimate messages. We’ve seen phishing emails that perfectly mimic invoices, shipping notifications, password reset requests, and even messages that appear to come from your CEO.
The basic mechanics haven’t changed much (attackers still want your credentials, personal information, or access to your systems), but their methods have evolved. Modern phishing attacks use generative AI, real company logos, accurate employee information (often scraped from LinkedIn), and messaging that’s relevant to your actual job functions.
Phishing ultimately targets the psychological factor. These attacks are engineered to bypass logical thinking by triggering emotional responses: urgency, fear, curiosity, or authority. When you receive an “urgent security alert” or a “final notice” from what appears to be your bank, your emotional brain often reacts before your analytical brain can catch up.
Phishing now comes in several flavors, each more targeted than the last:
- Spear phishing: Attacks customized for specific individuals using personal details.
- Whaling: Targeted specifically at executives and high-value employees.
- Business email compromise (BEC): Impersonating executives to authorize fraudulent transactions.
- Clone phishing: Duplicating legitimate emails but replacing links or attachments with malicious ones.
The most dangerous aspect of phishing isn’t its technical sophistication—it’s how it exploits human trust. We’re conditioned to respond to emails from our colleagues, service providers, and especially our leadership. Attackers know this and design their messages to slip past our natural suspicion.
8 ways to spot phishing emails instantly
Most phishing emails contain some sort of telltale sign that can help you identify them before disaster strikes. The challenge is knowing exactly what to look for, and that’s the digital equivalent of spotting a counterfeit bill. Here are the red flags that give away even the most convincing phishing attempts:
- Suspicious sender addresses: Always check the actual email address, not just the display name. Scammers often use domains that look legitimate but contain slight misspellings (like arnazon.com instead of amazon.com) or add extra words (like amazon-secure-notification.com).
- Urgent action required: Phishing emails frequently create artificial time pressure to short-circuit your critical thinking. Messages claiming “Your account will be suspended in 24 hours” or “Immediate action required” are classic pressure tactics designed to make you act before you think.
- Unexpected attachments: Be extremely wary of email attachments you weren’t expecting, especially if they have unusual file extensions (.zip, .exe, .js). These often contain malware that activates when opened.
- Suspicious links: Hover over links without clicking to see where they actually lead. If the displayed text says “bankofamerica.com” but the actual link shows “bank0famerica.co” or a string of random characters, you’re looking at a phishing attempt.
- Grammar and spelling errors: Yes, attacks have improved, but many phishing emails still contain awkward phrasing, unusual salutations (“Dear valued customer”), or spelling mistakes that legitimate organizations would catch.
- Generic greetings: Legitimate organizations that have your information typically address you by name. “Dear user” or “Valued customer” often signals a mass phishing campaign.
- Requests for sensitive information: Legitimate companies never request passwords, Social Security numbers, or full credit card details via email. Any message asking for this information is almost definitely fraudulent.
- Too good (or bad) to be true: Whether it’s an amazing offer, an unexpected refund, or a terrifying warning, emails that trigger strong emotional responses warrant extra scrutiny. Phishers rely on emotions overriding logic.

Advanced phishing detection strategies
The basic red flags help catch obvious attempts, but smart phishing attacks demand a bit more know-how. We’ve found that combining multiple verification methods creates the strongest defense against even the most convincing scams.
The most powerful technique remains the “out-of-band” verification. This means contacting the supposed sender through a different channel than the email itself. If you receive a suspicious request from your CEO, send them a text or walk to their office instead of replying to the email. This simple step defeats even the best-of-the-best impersonation attempts.
Next, do some email header analysis. The “Received:” fields in an email’s full headers reveal the actual journey the message took to reach you, and this often exposes inconsistencies. While not everyone needs to become a header expert, knowing how to access this information (usually through the “view original” option in your email client) gives you an advantage.
Modern link scanning tools don’t just check against known bad URLs. Now, they open links in secure sandboxes to observe behavior before you risk your actual device. Many organizations use these at the gateway level, but individual browser extensions can provide similar protection.
The best strategy combines technological solutions with human awareness. Neither works well without the other. Advanced phishing can bypass technical controls, and even alert humans miss things without supportive technology. The intersection is where real security happens.
What to do when you spot a phishing attempt
Spotting a phishing email is just the first step. Don’t just delete it and move on (though that’s better than falling for it).
First, don’t interact with the message at all. Don’t click links, download attachments, or reply. If you’ve already clicked something, disconnect from the network immediately and contact your IT security team.
Report the phishing attempt through proper channels. Most email clients now have a “Report Phishing” button, and your organization likely has a specific reporting process. This helps protect others and improves detection systems.
For business-critical phishing (like CEO impersonation or vendor fraud), alert your security team immediately. Seriously, minutes can make the difference in preventing financial damage.

If the phishing attempt impersonated a specific company, consider reporting it directly to them. Most major organizations have dedicated security@company.com addresses exactly for this purpose.
The actions you take after spotting phishing don’t just protect you. They also strengthen the entire security ecosystem.
Phishing prevention techniques (that actually work)
There’s no single solution that provides perfect protection, but layering these techniques creates a defense that catches what individual measures might miss:
- Email authentication standards (DMARC, SPF, DKIM)
- Multi-factor authentication
- Security awareness training
- Email filtering solutions
- Zero trust security model
- Browser email security solutions
Email authentication standards
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) works by verifying that incoming emails actually come from where they claim to. It prevents exact-domain spoofing to make it impossible for scammers to send emails that appear to come from your exact domain.
A properly configured “p=reject” policy means emails that fail authentication (SPF or DKIM) are blocked before reaching inboxes. This eliminates an entire category of phishing attacks. Plus, DMARC’s reporting capabilities shows who’s legitimately sending email using your domain versus who’s trying to impersonate you.

Multi-factor authentication
Even if credentials are phished, MFA provides a second line of defense. Requiring something you have (like a phone) in addition to something you know (your password) stops most credential-based attacks early. The most secure forms now use push notifications, authenticator apps, or physical security keys (rather than SMS).
Security awareness training
Traditional security training fails because it’s boring and infrequent. Better training programs use simulated phishing attempts sent regularly throughout the year to provide immediate feedback when employees fall for them. This experiential learning creates lasting behavior change in ways that videos and quizzes just can’t.
Advanced email filtering
Modern email security gateways go far beyond basic spam filtering. They use machine learning to detect anomalies in message content, sender behavior, and attachment characteristics. These systems can identify and quarantine phishing attempts that would fool human recipients, especially when you train them on your organization’s specific communication patterns.
Zero trust approach
The zero-trust model operates on a simple principle: trust nothing, verify everything. This means treating all email as potentially malicious (regardless of source). Implement controls like link sandboxing (where URLs are tested in isolated environments before users can access them) and strict attachment policies.
Browser email security solutions
Browser-based protection warns users when they attempt to visit known phishing sites or download suspicious files. Most of these solutions now offer real-time protection by checking URLs against constantly updated threat intelligence databases.
Follow this phishing protection checklist
Unfortunately, phishing protection is never one-and-done. It’s an ongoing commitment. Here’s where you can start:
- Check your domain’s email authentication: Use Valimail’s free Domain Checker to see if your current email authentication setup is actually protecting you from impersonation attacks.
- Implement DMARC with proper enforcement: Move beyond “monitoring mode” to an actual enforcement policy (p=quarantine or p=reject) that blocks fraudulent emails. This step alone eliminates an entire category of phishing threats.
- Monitor your email ecosystem: Sign up for Valimail Monitor (it’s free) to get visibility into who’s sending email using your domain (both legitimate senders and potential attackers).
- Automate your DMARC management: Consider Valimail Enforce to eliminate the technical complexity of DMARC implementation and maintenance.
Email security isn’t about perfection. It’s about making your organization a harder target than others. And the steps you take today are what determine if you survive an attack tomorrow.